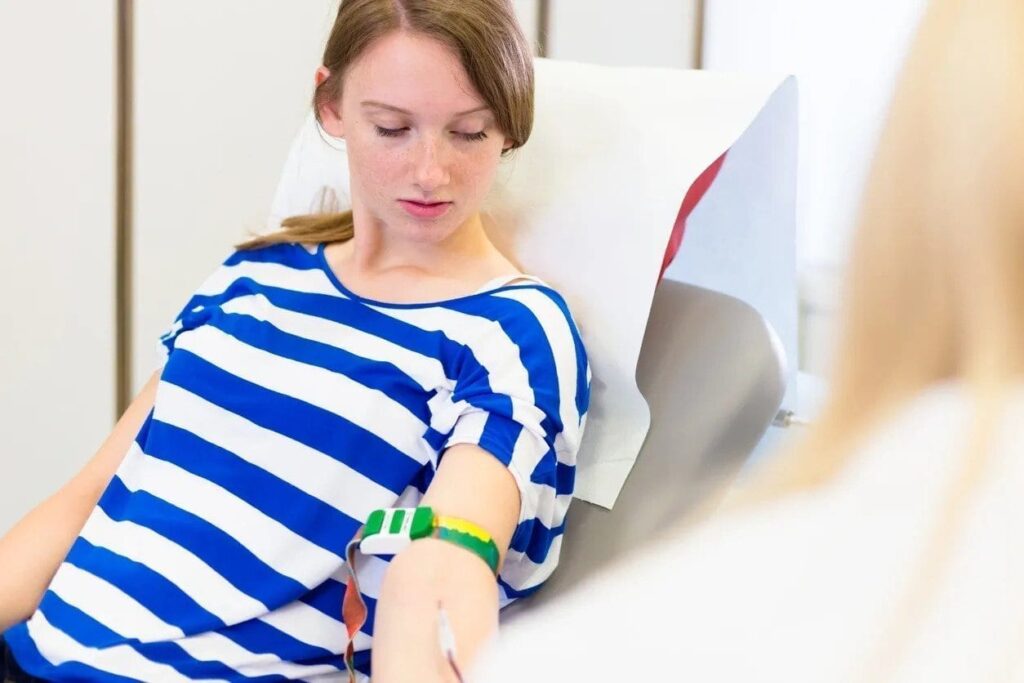

THE SCIENTIFIC BENEFITS OF BLOOD DONATION
This brings us to the topic of blood fluidity and precisely what it means.
Blood fluidity is the ability of blood to flow without any obstruction throughout the body. To stay healthy, blood flow shouldn’t only be useful in veins and large arteries. The blood flow should be equally smooth in the smaller blood vessels, such as capillaries.
In these capillaries, oxygen finds a place to stay while carbon dioxide is removed. It’s also where the exchange of nutrients occurs. If one wants to optimize their overall health, they will first need primal blood circulation. There are plenty of ways to improve blood circulation in a person. For one, a person can start by lowering their blood sugar intake and eating more beans. Simple changes in the lifestyle can be perfect for blood circulation.
How To Improve Blood Fluidity?
One of the most effective ways to increase blood fluidity is to allow yourself to have a better diet. Let’s take a look at some changes you can make in your food consumption.

BENEFITS OF BLOOD DONATION
1. Stay Away From Alcohol
We aren’t saying that you should forego alcohol entirely; however, excessive amounts of it can certainly be harmful to your health, especially the heart. If you have been drinking alcohol regularly, it is about time you cut back.

2. Drink Water
Water will never be an underrated element for the human body. The secret behind staying healthy will always be in some ways tied to drinking water.
As for our organs, they can only function properly when they are hydrated. Water helps us flush out the toxins. It also makes the blood circulation better, thus allowing us to avoid any possible health hazards. It’s recommended to consume half your body weight in ounces.

3. Go Nuts!
Consuming healthy nuts such as walnuts and almonds can be great for one’s blood flow. Specifically, you should focus on nut families with high vitamin content in the A, B, C, and E groups. Nuts that have a high amount of iron and magnesium are also good sources. The circulation in a person’s body is improved with nuts reducing the inflammatory content and oxidative damage the arteries face.

4. Go, Green!
Or in this case, make green tea a part of your daily diet. If you are a tea addict, well, we won’t stop you from drinking it. However, instead of milk tea, how about switching to its healthier version? Green tea can be an excellent friend when it comes to stimulating the functions in a person’s body. The magic of green tea is that it can widen the blood vessels in a person’s body. The wider the blood vessels, the better the blood flows a person has.

5. Keep Away From Stimulants
Stimulants are bad for blood circulation. Caffeine and sugar can be especially harmful. If you reduce these two stimulants’ intake, your blood will circulate through your body better and face lesser obstruction.
Sugar and caffeine are primarily responsible for dehydrating a person’s body. As we previously discussed, when your body is dehydrated, your organs don’t work the way they should. Another unexpected way to have better blood fluidity is to donate some blood.
Now, how to benefit from donating blood!
The fantastic thing about blood donation is that it isn’t only beneficial for the recipient. Other than the joy that comes from reaching out and helping another person, donors benefit physically from blood donation.
Let’s take a look at some of these unexpected perks.
1. Prevention Of Hemochromatosis
One of the benefits a person can get from donating blood is reducing the risk of getting Hemochromatosis. This is a particular category of health condition in a person when they have an excess amount of iron content in their body. This could be a genetic disorder caused by excess alcohol intake, anemia, or other health conditions. When a person participates in donating their blood from time to time, it helps them cut down on the body’s iron intake. Of course, a person can only donate blood if they first match the standard blood donation criteria.

2. Yes A Reduced Risk Of Cancer
It has been suggested that blood donation can help reduce the chance of a person getting cancer. This is similar to how donating blood helps with Hemochromatosis. The iron in the blood stays balanced when a person donates blood regularly. A lower level of iron in the body has also been linked with lower cancer risk.

3. Keep Your Heart Healthy
Again, when a person donates blood, they eliminate the possibility of absorbing an excessive amount of iron. This, in turn, keeps certain heart and liver conditions in check, which can be caused by high iron content. When a person’s diet has too much iron content, the body doesn’t know how to absorb it properly. The extra iron left usually gets stored in a person’s pancreas, heart, and liver. When these organs have so much iron in them, their bodies become at risk of liver failure and cirrhosis. They can also sustain pancreatic damage and face heart conditions such as arrhythmic heartbeat. A person would be getting rid of a lot of possible diseases by donating blood.

4. Assists in Weight Loss
Regularly donating blood is a beautiful way of reducing the total weight of a person by a little. The people who have to deal with obesity can make them closer to the chances of developing some heart disease and other similar disorders. However, the person donating the blood shouldn’t go overboard. It shouldn’t be far too often to lose weight. A person should always get a proper checkup first to make sure they are fit to donate blood.
5. Boost Blood Cells Production
Once the body loses blood, it quickly tries to make up for the blood it has lost. This leads to the body producing newer blood cells. New blood cells are an excellent way to keep the inner workings of the body fresh and healthy.

6. Helps Lower Blood Sugar
Which is one of those things a lot of people are unaware of. When we have too much sugar in our system, we end up increasing the triglycerides count. Triglycerides are a blood fat of sorts. The rise in triglycerides leads to an inevitable reduction of blood fluidity. As such, sugar doesn’t have the best reputation, and if we look at how it affects blood fluidity, it’s well deserved. The sugar-sweetened drink that people keep on drinking doesn’t help the cause either.
These days, most people aren’t necessarily intaking sugar directly in their diet, but getting it from hidden sources such as drinks with high sugar content in them or food you don’t know has sugar in the ingredient list. It’s essential to do a thorough check before you consume anything. Thankfully, when a person donates some of their blood, they end up donating some of the blood fat in the body as well. A reduction of blood sugar quickly leads to better circulation in the system, which keeps the human body healthy.
On that note, other than donating blood, it’s also an excellent idea to make beans a regular part of your diet. The fiber found in beans is exceptionally useful in keeping diabetes under control. Beans have different kinds of phytochemicals. This phytochemical improves blood flow. The type of beans you are using for the diet isn’t a matter either. It could be lentils, kidneys, or peas, and they would all help the overall blood flow in your body.

7. Improves Brain Function
It has recently been suggested that blood fluidity might be the missing link involved in improving blood functions. Evidence suggests that it doesn’t matter whether you are old or young or already have developed dementia; if you enhance your blood flow, your brain functions will see definite improvements.
Are There Any Risks Associated With Blood Donation?
For a healthy adult, blood donation is usually considered a safe practice. A person donating blood doesn’t have to worry about somehow contracting any disease from any previous donors. For every donor, the equipment used to draw blood is thoroughly sterilized and new.
Certain people experience sudden bouts of dizziness, nausea, or a feeling of light-headedness after they have donated blood. It doesn’t last for too long, though, if it does happen. At most, this kind of dizziness stays for some minutes before the person can function properly again. If the person feels nauseous, it’s better to lie down and have your feet raised until they feel in control of their body again.
The Blood Donation Procedure
First, you need to register as a donor. The procedure includes providing proper identification as to who you are, your previous medical record, and letting the blood donation center do a quick physical examination to determine you are a healthy individual. The center might also give you some pamphlets or a book containing information about blood donation, how it benefits you, and the person receiving the blood. Once they have tested your blood sample and determined you are eligible, they will begin the process of blood donation.
There are different kinds of blood donation procedures, but whole blood donation is the most common one. This is because it comes with maximum flexibility. Once the blood donation occurs, the doctor can use the blood to either transfuse it in pure form or specifically use the platelets, red cells, and plasma, depending on the recipient. In the whole blood donation process, the person is first provided a reclining chair they can sit in. It is up to the donor whether they want to donate the blood while sitting or in a flat, upright position.
After you have donated your blood, the center will provide you with snacks and drinks to replenish your body. After you have eaten your food and taken at least 10 to 15 minutes of rest, you can leave the center. There are cases where the person might feel faint. They only need to tell the staff, and arrangements will be made to lie down until they are feeling better.
What should A Blood Donor Know?
There are certain things a blood donor should be aware of before they proceed with the blood donation process. For one, the donor should be at least 17 years old before they are eligible for blood donation. Though, there are states that have no problem with 16-year old donating blood.
The person donating blood should be overall in good health. It would be good if they are at least 110 pounds in weight. The person should also have their medical record ready and list the medicines they have taken previously. Depending on the kind of medical condition a person has, the chance that they would be allowed to donate blood lessens.
After you have donated whole blood, there should be an 8-week gap before your next donation. Some people might feel nervous about donating blood, especially if their first time. There are certain things you can do to make the process easier. Before your blood donation appointment, make it a point to drink at least 16 ounces of water.
Final Thoughts
Hemorheology is a branch of science that has been received quite well by the health community. Some physicians and scientists dedicate all their time to studying blood fluidity. Part of it is due to the connection that has been established between better blood fluidity and the prevention of cancer. Yet, a part of society is blissfully unaware of these branches of science. While scientists continue to research blood fluidity, it is your job to keep yourself healthy and follow these instructions to do the same.
References
1. Advantages and disadvantages of donating blood (Rachel Nall, September 12, 2017,pp13-16)
2. The benefits of donating blood ( Alana Biggers, June 26, 2019, pp 2-8)
3. Hematological, biochemical and antioxidant indices variations in regular blood donors among Mediterranean regions (Tsamesidis et al., 2019, p 3-6)
4. American Journal of Epidemiology (pp 36-39)
5. Who can’t donate blood? ( Sharon Orange, January 2015, pp3-5)
6. A journal on Iron disorders by Institute Patient Information Series (2010)
7. 6 Surprising health benefits of donating blood ( Brianna Flavin, February 01, 2018, pp6-7)
8. Benefits of donating blood (published by National Blood Transfusion Service, June 17, 2015)
