Live Longer By Reducing Oxidative Stress!
By Brian James Rose
A lot of metabolic processes happen inside the body. These processes are absolutely necessary for all cells to survive. The exchange of nutrients occurs every minute of the day and these nutrients get consumed to provide energy from their breakdown. As a result of this breakdown, a lot of metabolic waste is generated.
As the demand for energy increases, the breakdown increases which ultimately results in the excessive production of toxins inside the body as waste. One of the said toxins is ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species). These are a group of ions containing oxygen that float in the system. ROS can either help neutrophils and macrophages with their ability to kill pathogens or do the complete opposite and destroy normal functioning cells of the body. These ions can be neutralized by their counteracting compounds; antioxidants. Less amount of antioxidants in the body can indirectly cause a lot of harm to the cells of the body.
What is oxidative stress?
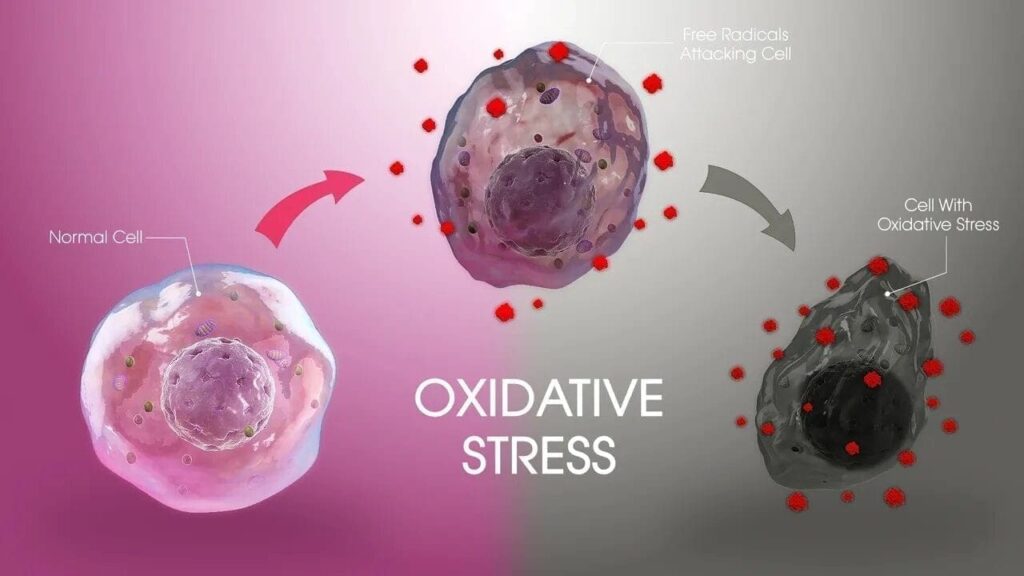
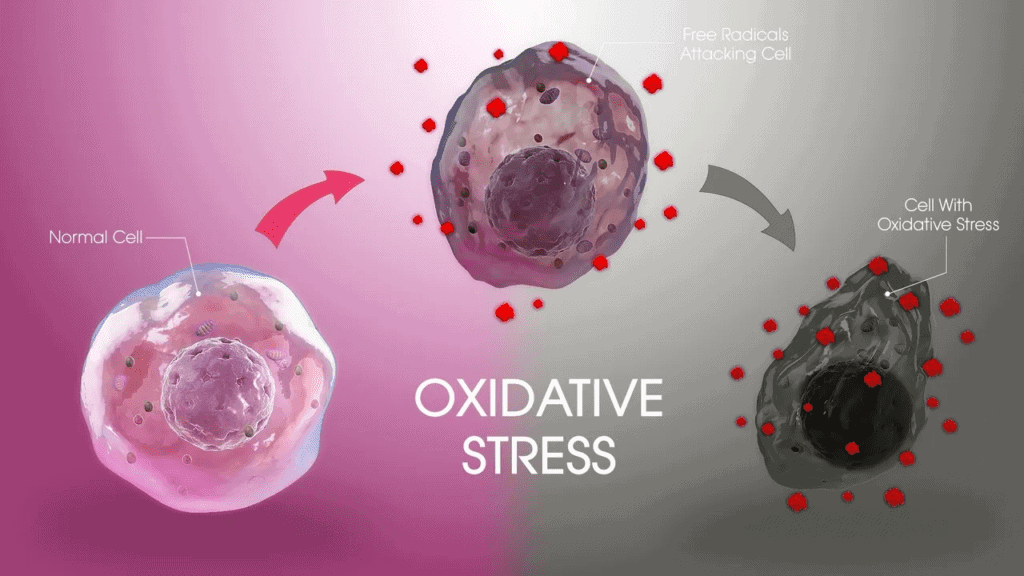
Whenever the levels of ROS increase and antioxidants decrease; the body is said to be in a state of oxidative stress. Small quantities of these free radicals (ROS) are formed physiologically, which is countered by the body’s defense antioxidant pathway. However, with senescence and chronic diseases, these free radicals are produced in excess without enough antioxidants present to neutralize them.
It can happen due to a variety of reasons; it can either be due to excessive production of ROS from mitochondria to cover up needs of aerobic respiration or through exogenous sources such as environmental pollution or radiation. This state is extremely dangerous for the body if it exists for a long time as it can cause a lot of harm to the tissues. It not just promotes the process of aging but also results in excessive damage to the cells. In order to rid the body of this condition, it is important that antioxidants supersede the effects of either endogenous production or exogenous administration.
Hydrogen as an antioxidant
Hydrogen has been identified for its therapeutic effects since 1888 in the world of medicine, but with more research, it was found that this gas could help in a number of degenerative diseases owing to its antioxidant properties especially because hydrogen gas is present in the environment in abundance. Its composition is such that it is not only non-toxic, non-metallic, odorless, but it is also very light. Much of its antioxidant properties come from its small structure.
The H2 gas molecule has the ability to cross membranes with ease. It consists of two electrons in its outermost shell, therefore, whenever it comes across a free radical, it neutralizes it. Most of these free radicals are hydroxyl ions (OH-) or peroxynitrite ions (ONOO-). These ions are formed as a result of oxidative metabolism. Antioxidant properties provided by hydrogen molecules save many cells from the destructive effects of these free radicals. These ions have the ability to damage mitochondrial DNA, which leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and ultimately apoptosis of that cell.
When hydrogen reacts to these molecules, it converts them into their nonreactive counterparts. This helps relieve off the oxidative stress on the body. A study conducted in 2012 on animal models in order to assess the therapeutic and antioxidant properties of hydrogen gas showed conclusive data. It was proved that hydrogen gas indeed helps in the reduction of hydroxyl ions as seen in male germ cells of mice as well as in the retinas of rats.
Hydrogen and its therapeutic effects
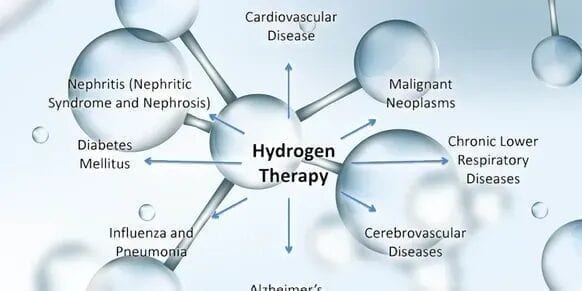
Many animal models have been used to testify the antioxidant and therapeutic effects of hydrogen including mice, rodents, rabbits as well as pigs. It has also been shown to be helpful in the growth as well as the regulation of hormones and cytokines in plants. Apart from it helping in decreasing oxidative stress and the damage that is induced due to it, it is can also be seen to play a positive role in a lot of diseases such as;
1. Ischemia or reperfusion injury
Ischemia is the decreased supply of blood to an organ or tissue. When that happens, the cells of that region suffer from oxidative stress. When the supply restores, the tissue undergoes reperfusion injury due to the sudden turbulent flow of blood in that area, causing an outburst of free radical production. Due to this, inflammatory processes are marked in these regions.
However, molecular hydrogen has been seen to exhibit cytoprotective properties and helps neutralize free radicals formed after reperfusion injury.
Several animal models have been tested to see its efficacy, especially in the heart. Ischemia in the vessels of the heart is very common and can have fatal consequences. Administration of hydrogen gas to combat the amount of damage has been seen especially in rats by a study conducted in 2012 as published in the Journal of American Heart Association.
2. Metabolic diseases
It is a group of diseases that are present in an individual. They occur due to a number of risk factors such as; obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia as well as hypertension. All of these conditions increase the risk of stroke, type 2 diabetes mellitus as well as infarction. These string of pathologies are all linked to the increasing levels of oxidative stress on the body. A study conducted on rats in 2011, showed significant improvements with induced metabolic syndrome especially by enhancing the clearance of creatinine from the body.
3. Cardiovascular diseases
The entire cardiovascular system is pretty intricate and consists of endothelial cells, smooth muscles, as well as the blood circulatory system. Any kind of abnormality in the normal functioning of the body poses damage to the cardiovascular system. Dyslipidemia increased blood pressure as well as protein changes are all responsible for causing damage.
Hydrogen gas administration has been seen to reduce the effects of these pathologies. With the help of animal models, it was observed that through inhalation of hydrogen gas, injury to the heart muscles was reduced. It was also seen that hydrogen gas was helpful in the recovery of the left ventricular function, as well as reducing the size of the damaged tissue after an episode of infarction.
4. Neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases occur due to chronic loss of function of neurotransmitters, neurons, or neuronal circuits. These diseases include; Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) as well as Huntington’s. Chronic oxidative stress has been linked with the occurrence of Parkinson’s disease. The loss of substantia nigra linking to this disease is mainly due to mitochondrial dysfunction leading to the increased amount of free radical production. Administration of hydrogen in this regard has been seen to be beneficial, as seen in a trial conducted in 2013 on patients with Parkinson’s disease.
5. Infections
A lot of infections manifest inside the body and most of them harbor due to decreased immunity. In this case, when any pathogen gets inside, it causes systemic damage to fatal consequences. Failure of an antioxidant system with oxidative stress increase due to the development of sepsis results in mitochondrial damage, cell death, and the release of inflammatory compounds. These inflammatory cytokines also end up damaging more cells of the body.
Hydrogen gas treatment has shown improvements in recovery from infection by lowering the production of cytokines as seen in animal models. Hence, if administered in patients suffering from an infection, it can show remarkable improvements in the overall recovery phase of these patients.
6. Cancer treatment and radiation
Hydrogen treatment has shown marked improvement in saving healthy cells from radiation therapy. These radiations are given to cure cancer and most often result in killing off healthy cells, compromising the health of the patient. The administration of hydrogen can help reduce the damage by reducing the number of free radicals produced from the emissions of chemotherapy and radiation. A clinical trial conducted on 49 patients with hepatocellular cancer, who were given hydrogen water showed improved results in their overall side effects; including fatigue, diarrhea, hair loss, and depression.
7. Aging and skin;
Aging is accompanied by a lot of pathologies and a lot of breakdowns. This breakdown is usually the result of excessive free radical production (ROS), further manifesting the process of degeneration of cells. Antioxidant properties of hydrogen can be used in helping combat some of the many effects of aging on the body; such as the use of hydrogen gas on the skin. Hydrogen water used for bathing can act by strengthening the collagen fibers of the skin and decreasing wrinkles. Experiments on rat models also showed that the use of hydrogen water helped skin with cutaneous burns.
Methods of hydrogen administration
Hydrogen can be administered in the body through a number of routes. It can either be used as an injectable, with hydrogen gas dissolved in saline water. It can also be administered in the body through its inhalation or by simply drinking water with dissolved hydrogen gas. Hydrogen that is orally administered is not very beneficial as it does not have the potential to detoxify ROS from diseased tissues.
Safety of hydrogen gas
Hydrogen has been used for decades without showing any signs of toxicity. It is actively used as a mixture given to divers to deep-sea divers to prevent decompression sickness. A study conducted on rats that were fed hydrogen-induced water for a year showed no changes in their systems. Hence, hydrogen gas has not been associated with toxicity even when used in high concentrations marking it pretty safe to be used.
Conclusion
With the amount of wear and tear that occurs in the body, most often our bodies undergo oxidative stress. The body can only rid itself off of it if there is an apt antioxidant system functioning in the body. The demand for these antioxidant compounds varies considerably and hence it is mostly insufficient in overcoming the damage caused by these free radicals.
A solution to overcome this crisis of oxidative stress, hydrogen molecule therapy has been seen to act as a potent antioxidant through its reducing action. It helps restore the normal functioning of the body through redox reactions. It is highly permeable and can easily cross membrane barriers and travel from one fluid compartment to another.
Apart from its short-term benefits, hydrogen administration has been seen to be helpful in walling off damage caused by a lot of diseases. It is seen to help in damage caused by injuries, as well as inflammatory, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative diseases.
It has also been shown to exhibit weak oxidative stress, which helps in the body’s own adaptive response towards the insult. It has also been shown to regulate gene expression.
With a lot of benefits seen by this simple gas, a lot of research is still being carried out to assess its full potential. Once it is established, it is expected to help manage many acute and chronic illnesses, improving the quality of life markedly in patients who otherwise need years-long therapy and medications to get stable.
References
- Nicolson GL, de Mattos GF, Settineri R, Costa C, Ellithorpe R, Rosenblatt S, La Valle J, Jimenez A, Ohta S. Clinical effects of hydrogen administration: from animal and human diseases to exercise medicine. International Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2016;7(01):32.
- Yoritaka A, Takanashi M, Hirayama M, Nakahara T, Ohta S, Hattori N. Pilot study of H2 therapy in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. Movement Disorders. 2013 Jun;28(6):836-9.
- Hashimoto M, Katakura M, Nabika T, Tanabe Y, Hossain S, Tsuchikura S, Shido O. Effects of hydrogen-rich water on abnormalities in an SHR. Cg-Lepr cp/NDmcr rat-a metabolic syndrome rat model. Medical Gas Research. 2011 Dec;1(1):26.
- Hayashida K, Sano M, Kamimura N, Yokota T, Suzuki M, Maekawa Y, Kawamura A, Abe T, Ohta S, Fukuda K, Hori S. H2 gas improves functional outcome after cardiac arrest to an extent comparable to therapeutic hypothermia in a rat model. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2012 Oct 16;1(5):e003459.
- Ohta S. Molecular hydrogen is a novel antioxidant to efficiently reduce oxidative stress with the potential for the improvement of mitochondrial diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects. 2012 May 1;1820(5):586-94.
- Poljsak B. Strategies for reducing or preventing the generation of oxidative stress. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity. 2011 Dec 10;2011.
- Murakami Y, Ito M, Ohsawa I. Molecular hydrogen protects against oxidative stress-induced SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell death through the process of mitohormesis. PLoS One. 2017;12(5).
- Chuai Y, Gao F, Li B, Zhao L, Qian L, Cao F, Wang L, Sun X, Cui J, Cai J. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates radiation-induced male germ cell loss in mice through reducing hydroxyl radicals. Biochemical Journal. 2012 Feb 15;442(1):49-56.
**Disclaimer**
This site and its services are for consumer educational use only. Nothing contained in this article is or should be considered or used as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Never start any diet, exercise, or supplement program without consulting your medical provider. This article and its services do not constitute the practice of medicine. Users should always seek the advice of a physician with any questions regarding their health or medical conditions. Never disregard, avoid, or delay obtaining medical advice or following the advice of a physician because of something you have seen or read on this site.
