
How Rockefeller Monopolized Medicine and Created BIG Pharma!
In 1839, John D. Rockefeller was born into a poor family. He was the son of a traveling snake-oil salesman who claimed to be a doctor and his strict and devout wife, who brought him up in the Baptist Church. The family ultimately made their home in the Cleveland suburbs, Ohio, where John dropped out of high school and began working as a bookkeeper at the age of 16. He initially traded in the hay, grain, meats, and other items, but in the early 1860s, as oil output in western Pennsylvania increased, he made the decision to enter the oil industry. [3] He would spend months at a time traveling from town to town in the West before returning to the family’s residence with substantial sums of money. Eliza Davison Rockefeller, his mother, was a strict and devout person. She taught John how to work, to save, and donate to organizations. [1] Figure.1

Figure 1: John D. Rockefeller
Industrial Empire of John D. Rockefeller
Standard Oil, in full Standard Oil Company and Trust, an American company and corporate trust that from 1870 to 1911 was the industrial empire of John D. Rockefeller and associates, controlling almost all oil production, processing, marketing, and transportation in the United States. The company’s origins date to 1863, when Rockefeller joined Maurice B. Clark and Samuel Andrews in a Cleveland, Ohio, oil-refining business. In 1865 Rockefeller bought out Clark, and two years later he invited Henry M. Flagler to join as a partner in the venture. By 1870 the firm of Rockefeller, Andrews, and Flagler was operating the largest refineries in Cleveland, and these and related facilities became the property of the new Standard Oil Company, incorporated in Ohio in 1870. By 1880, through the elimination of competitors, mergers with other firms, and the use of favorable railroad rebates, it controlled the refining of 90 to 95 percent of all oil produced in the United States. Founded in 1882, Standard Oil of New Jersey was one component of the trust; by design, the Standard Oil Trust embraced a maze of legal structures, which made its workings virtually impervious to public investigation and understanding. In 1899, however, the company renamed its New Jersey firm Standard Oil Company (New Jersey) and incorporated it as a holding company. All assets and interests formerly grouped in the trust were transferred to the New Jersey Company. Although consolidation did advance the large-scale production and distribution of oil products, many critics believed that the resulting concentration of economic power was becoming excessive. [26] Figure 2.

Figure 2: Standard Oil Company
John D. Rockefeller, a billionaire, is still one of the wealthiest people alive today. He emerged from humble origins to establish Standard Oil in 1870, and then ruthlessly set about eliminating his rivals to establish a monopoly of the oil business. In addition to iron, steel, and copper, he also ventured into railroads, general stores, and newspapers. In order to break up Standard Oil, the American government created the Sherman Antitrust Act in 1890. This set off a protracted legal struggle that the government eventually won in 1911. His goal of complete control came into conflict with this law. [2]
The Rockefeller Foundation played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of modern medicine. By the early 20th century, the foundation began heavily funding medical schools, with a strong bias towards allopathic medicine. This strategic funding aimed to potentially restructure medical education, emphasizing pharmaceuticals and patented treatments over traditional, natural healing modalities like herbal medicine.
This shift had profound implications. Medical students became primarily trained in what we now consider Western medicine, with its focus on diagnosing and treating disease using drugs and surgery. The Rockefeller influence arguably marginalized alternative approaches, reshaping the public’s perception of human health and laying the groundwork for the rise of today’s massive pharmaceutical industry, often referred to as “Big Pharma.”
This restructuring of medical education (also taught allopathic medicine), influenced by Rockefeller funding, went hand-in-hand with the growing power of the American Medical Association (AMA). The AMA further solidified the dominance of allopathic medicine, actively discrediting alternative medicines and the practitioners who offered them. This coordinated effort ultimately transformed the landscape of American healthcare, prioritizing a medical model that would become heavily reliant on the pharmaceutical industry.
Standard’s Oil Monopoly
In the early 1900s, Standard Oil Co., chaired by John Rockefeller, was a powerful monopoly dissolved by SCOTUS. At the beginning of the 20th century Standard Oil Co. was one of the world’s largest and most powerful corporations and its chairman, John D. Rockefeller, was the first billionaire. While people were divided about whether monopolies were good for society, exposés by the muckraker Ida Tarbell detailing the company’s strong-arm practices against rivals, railroad companies, and others eventually turned public opinion against it. In 1911 the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that Standard Oil Trust be dissolved under the Sherman Antitrust Act and split into 34 companies.
The Sherman Anti-Trust Act of 1890 affected Rockefeller Family
Standard Oil Co. of New Jersey v. United States (1911) is a U.S. Supreme Court case holding that Standard Oil Company, a major oil conglomerate in the early 20th century, violated the Sherman Antitrust Act through anticompetitive actions, i.e., forming a monopoly, and ordered that the company be geographically split. Figure 3.

Figure 3: The Sherman Anti-Trust Act
The Standard Oil Company of New Jersey was, in fact, a holding company which the Rockefeller family held. The Rockefeller family organized their oil empire by creating such holding companies in many of the jurisdictions in which they operated. In total, the Rockefeller family and their holding companies controlled almost the entire petroleum market in the U.S. To further the Rockefeller’s control over the petroleum market, the Standard Oil Company of New Jersey had acquired nearly all of the oil refining companies in the United States. The United States brought suit against the Standard Oil Company of New Jersey, alleging that it violated the Sherman Antitrust Act because its acquisitions were an undue restraint of trade.
The Court first ruled that Congress had the power to pass the Sherman Antitrust Act under the Commerce Clause of the Constitution. It then ruled that “restraint of trade” included monopolistic behavior, and only unduly restrained trade if it led to one of the three possible consequences: higher prices, reduced output, and reduced quality. Balancing antitrust protections with principles of freedom of contract, the Court ruled that a company’s potentially monopolistic actions could only be illegal if it led to one of those three consequences. In this case, however, the Court found that Standard Oil of New Jersey’s actions led to these consequences and therefore violated the Sherman Antitrust Act. [28]
Following new petroleum discoveries in the United States and abroad, independent oil companies finally brought real competition to the medical industry. But the former Standard Oil companies, with modern names like Exxon, Mobil, Amoco, Chevron, ARCO, Conoco, and Sohio, continued to exercise significant influence on oil pricing.
When the Supreme Court broke up the Standard Oil Trust in 1911, electric lights were rapidly replacing kerosene lamps. But the gasoline-driven automobile was just beginning to appear. Gasoline, up to that time a useless byproduct of oil refining, made the companies formed from the trust wealthier than they had ever been. Rockefeller, owning a 25 percent share in each of the new companies, was worth $900 million in 1913 ($13 billion in today’s dollars). This made him the richest man in the world.
In retirement, Rockefeller made a science of philanthropy. He and his son gave away most of the Rockefeller millions, mainly to medical research, public health, and educational institutions. Even so, he bitterly objected to the federal income tax when it began in 1913.
Economist Robert Heilbroner once described John D. Rockefeller as “an agent for better and worse in the immense industrial transformation of America.” Outliving most of his business associates and critics, John D. Rockefeller died in 1937, a few weeks short of his 98th birthday.[29] Figure 4

Figure 4: Economist Robert Heilbroner
The U.S. Congress passed the Sherman Anti-trust Act of 1890 as the first law outlawing trusts. It bears the name of Senator John Sherman of Ohio, who served as Secretary of the Treasury and Chairman of the Senate Finance Committee under President Hayes. According to the Sherman Anti-Trust Act, the federal government may file lawsuits against trusts in order to dissolve them. Any arrangement “in the nature of trust or otherwise which was in hindrance of trade or commerce among the different states, or with foreign powers,” was deemed unlawful. [24] Figure.5

Figure 5: John Sherman
How Rockefeller targeted Medicine
At the time, ‘petrochemicals,’ or chemicals generated from oil, were being discovered and created in the US. Rockefeller saw an opportunity to grow his empire when it was discovered that prescription medications could be manufactured from oil. The secret was that, unlike traditional health cures, petrochemicals could be copyrighted, creating a huge prospect for Rockefeller profits. So, he turned to his close friend Andrew Carnegie, a fellow steel tycoon who had become wealthy through his monopoly and, coincidentally, one of the country’s foremost eugenicists. The two men came up with a scheme to take over American medicine together. Figure 6. [23]

Figure 6: Andrew Carnegie
In the early 1900s, natural and herbal treatments were immensely popular in America. Nearly half of the medical schools and practitioners in America used substantial knowledge from both European and Native American traditions while practicing holistic medicine. Rockefeller understood that eliminating the competition would be necessary for him to gain complete control of the medical sector. The first action Rockefeller took was to utilize his enormous riches (obtained from oil) to buy a portion of the German pharmaceutical company I.G. Farben. Figure 7.

Figure 7: IG Farben German University
Rockefeller recruited Abraham Flexner to attack on traditional medicine
Now that he was in charge of a pharmaceutical manufacturing business, he could carry out his strategy to oust the rivals. In 1910, Rockefeller recruited Abraham Flexner as a contractor to deliver a report to Congress in order to crush his rival. According to this report’s “conclusion,” there are too many medical schools and doctors in America, and all of the traditional natural healing methods that have been practiced for hundreds of years are unreliable. In accordance with the report’s recommendations, only the AMA (another monopoly) would be permitted to give medical school licensure in the United States. Figure 8.

Figure 8: Abraham Flexner
Rockefeller Monopoly against Traditional Medicine
Rockefeller ensured that his monopoly was protected when traditional natural medicines were expelled from medical schools by waging a focused disinformation campaign against his rivals. Through the press and other media of the period, homoeopathy and natural treatments were ridiculed and maligned. For employing natural medicine therapies, including ones that had been used safely and successfully for decades prior, too many doctors were even sentenced to prison. Medical colleges quickly began to resemble one another. The same allopathic system was taught to every student, and the definition of medicine changed to include the prescription of patented medications. American medicine adopted the philosophy of “a drug for every ill.” [4] Figure 9.

Figure 9: Traditional Medicine and Homeopathy
Rockefeller supported War against Natural Medicine in Australia
Around 400 high profile doctors, medical researchers and scientists recently joined forces to form lobby group Friends of Science in Medicine (FSM) in order to have “alternative medicine” degrees removed from Australian universities.
Chiropractic, osteopathy, Chinese medicine, naturopathy, iridology, kinesiology, reflexology, homeopathy, and aromatherapy are some of the courses on their blacklist.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 80 per cent of the world’s population relies on natural therapies. The figures in Australia are much the same. The argument that modern medicine is evidence-based as opposed to other types of medicine is an argument that is often used by medical lobbyists and tends to be generally accepted by the public. However, according to a report by a panel of experts assembled by the prestigious Institute of Medicine, “well below half” of medical care in the US is based on or supported by adequate evidence. Natural therapies have been used for more than 10,000 years, and so they deserve a place in society, in Australian universities, and even in modern medicine. According to Australian trauma and general surgeon Dr Valerie Malka, former director of trauma services at Westmead Hospital, while modern medicine is revolutionary when it comes to surgery, particularly in emergencies, for pretty much everything else, traditional, natural, or alternative medicine is much more effective. [5]
BIG Pharma Creation
Like any good monopolist, Rockefeller went further in seeking to consolidate his control. He took over the AMA and emboldened it as the gatekeeper of scientific thought and witch hunter of alternative medical practices. He took control of the FDA in order to control the approval process for new drugs. He even founded the American Cancer Society in 1913. Within a few short years, Rockefeller was in total control of the American medical system in both thought and action.
The result of this takeover, the product of this monopolist son of a conman and his eugenicist partner, would become known as “Big Pharma.” That Big Pharma took over and monopolized American medicine, promoting their own patented, profit-making products and suppressing all others, isn’t even a conspiracy theory. [23]
Big Pharma conspiracy theories
Big Pharma conspiracy theories are conspiracy theories which claim that the medical community in general and pharmaceutical companies in particular, especially large corporations, operate for sinister purposes and against the public good, that they conceal effective treatments, or even cause and worsen a wide range of diseases for the purpose of profitability, or for other nefarious reasons.[6][7] Some theories have included the claim that natural alternative remedies to health problems are being suppressed, the claim that drugs for the treatment of HIV/AIDS are ineffective and harmful, the claim that a cure for all cancers has been discovered but hidden from the public, claims that COVID-19 vaccines are ineffective, and that alternative cures are available for COVID-19. In each case the conspiracy theorists have blamed pharmaceutical companies’ search for profits. A range of authors have shown these claims to be false, though some of these authors nevertheless maintain that other criticisms of the pharmaceutical industry are legitimate.[8][9][10]
Rockefeller opposed Laetrile treatment for cancer
Laetrile is a word created from the first letters of laevorotatory and mandelonitrile and describes a semi-synthetic form of amygdalin. Amygdalin is a compound that can be isolated from the seeds of many fruits such as peaches, bitter almonds, and apricots. Both laetrile and amygdalin have a common structural component, mandelonitrile, which contains cyanide. Figure 10.
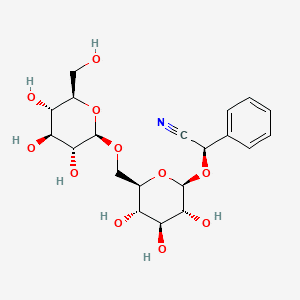
Figure 10: Amygdalin
Common Names of Amygdalin
- Apricot pits
- Vitamin B17
- Mandelonitrile-beta-glucuronide (semi-synthetic)
- Mandelonitrile beta-D-gentiobioside (natural product)
- Laevorotatory and mandelonitrile
- Prunasin
Potential Benefits of Laetrile
While most of the research on laetrile focuses on its effects on cancer, some studies have found that amygdalin, the natural form of laetrile, may have other health benefits.
Here are a few possible health benefits of amygdalin:
- It may lower blood pressure: In one study, amygdalin helped lower systolic blood pressure (upper value) by 28.5% and diastolic blood pressure (lower value) by 25%. These effects were enhanced when taken with vitamin C.
- It may relieve pain: Several animal studies show that amygdalin may help relieve pain caused by inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis. However, there is a lack of human-based evidence in this area.
- It may boost immunity: A test-tube study found that amygdalin improved the ability of immune cells to adhere to prostate cancer cells. [30]
Laetrile is known to have various side effects. Most of these side effects are caused by too much hydrogen cyanide in the body. That’s why the symptoms of laetrile poisoning are the same as cyanide poisoning.
Side effects include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Bluish skin caused by oxygen deprivation
- Liver damage
- Abnormally low blood pressure
- Droopy upper eyelid (ptosis)
Side effects are worsened by:
- Taking laetrile as a pill, rather than as an injection
- Eating raw almonds or crushed fruit pits while taking laetrile
- Taking too much vitamin C while taking laetrile
- Eating fruits or vegetables that may enhance the effects of laetrile, such as carrots, bean sprouts, celery, and peaches.
Research shows that vitamin C can interact with laetrile and increase its toxic effects.
Vitamin C speeds up the conversion of laetrile into hydrogen cyanide. It also depletes the body’s stores of cysteine, an amino acid that helps the body detoxify hydrogen cyanide. In some cases, taking laetrile (and amygdalin) has led to death through cyanide poisoning. [30]
The lack of laetrile’s effectiveness and the risk of side effects from cyanide poisoning led the Food and Drugs Agency (FDA) in the US and the European Commission to ban its use. However, it is possible to buy laetrile or amygdalin via the Internet. As there is no government control of these markets, preparations may not only come from questionable sources, but they may also be contaminated. Cancer patients should be informed about the high risk of developing serious adverse effects due to cyanide poisoning after laetrile or amygdalin, especially after oral ingestion. This risk could increase with concomitant intake of vitamin C and in vegetarians with vitamin B12 deficiency.
This systematic review found that there is no reliable evidence for the alleged effects of laetrile or amygdalin for curative effects in cancer patients. [12]
Laetrile, most trending traditional treatment for Cancer
Although the successful promotion of laetrile has occurred exclusively in the last 15 years, the material was first reported to be a cancer remedies about50 years ago. In the 1920s, working in a home laboratory to find a method for improving the taste of bootleg whiskey, an obscure San Francisco general practitioner, Dr. Ernst Krebs, Sr., suggested that an extract of apricot seeds reduced rodent tumors. [13] Figure 11.

Figure 11: Apricot Seeds
Dr. Krebs warned that the material, which in 1936 appeared to be predominantly the common chemical amygdalin was too unpredictable and too dangerous for general human use. Its promotion did not really begin until over 20 years later when hisson, Ernst Krebs, Jr. claimed to have synthesized a safe congener of amygdalin, for which he coined the term laetrile. Despite the younger Mr. Krebs’ claims, most of what has since been sold as laetrile has consisted of a variety of components and the active portion has usually been amygdalin itself. [14]
The promotion gained some momentum with the appearance of a Canadian adventurer, Andrew McNaughton, Jr., and the opening of a classic border clinic by a Mexican pathologist, Dr. Ernesto Contreras. The phenomenon was largely con fined to the West Coast and Mexico until the 1972 full-scale entry into the controversy by John Birch Society members in support of Birch activist, Dr. John Richardson. Dr. Richardson had been arrested for selling laetrile in violation of California law. Using the arguments and sophisticated political machinery of the far right and aided by the manpower of a large group of Americans caught up in a new religion of extreme food faddism, the pro motion rapidly swept across the country. [15] Figure 12.

Figure 12: Dr. Ernesto Contreras
Why Amygdalin got popular in America?
Amygdalin was first discovered in the early 19th century in France as an active component of several fruit pits and raw nuts. Cyanide, one of the main metabolites of amygdalin, was thought to have anti-cancer properties and was introduced in the United States in the 1920’s [16]. Several formulations of Laetrile have been used over the years, including oral, intravenous, peritoneal, and intramuscular preparations. The oral formulation is far and above the most potent, related to the metabolic activity of gut bacteria [17].
There are several theories explaining how cyanide could specifically target cancer cells, while leaving non-cancer cells unharmed. It has been proposed that cancer cells exhibit higher beta-glucuronidase activity, thus making them more susceptible to the uptake and hydrolysis of amygdalin to cytotoxic cyanide [16].
Another theory states that cancer develops as a result of specific vitamin deficiencies, and the addition of Vitamin B17 (Laetrile) can restore health to the body. Granted, these theories do have an experimental basis, however, the clinical evidence supporting the use of Laetrile as an anti-cancer agent is lacking. Laetrile is a compound that has been used as a treatment for people with cancer. Laetrile is another name for amygdalin. Amygdalin is a bitter substance found in fruit pits, such as apricots, raw nuts, lima beans, clover, and sorghum. It makes hydrogen cyanide which is changed into cyanide when taken into the body. Hydrogen cyanide is thought to kill cancer cells. Laetrile is also called Vitamin B-17, although it has not been approved as a vitamin by the American Institute of Nutrition Vitamins. [31]
Research on Laetrile
Some research suggests that B17 could be worthy of further study, but these studies have only been conducted on cells in a petri dish or on animals. That can be a start in laying the foundation for moving on to clinical trials involving people, but the research hasn’t advanced to that stage.
Some research on laetrile/amygdalin as a cancer treatment, published in reputable journals, does show promise. [18]
For example:
- In the March 2021 issue of the Journal of Biomelecular Structure & Dynamics, researchers say they uncovered the mechanisms by which amygdalin induces apoptosis—increasing one cellular protein and reducing another—as well as other beneficial actions at the cellular level. They state that “Amygdalin possesses anticancer properties and induces apoptosis,” and “Amygdalin can act as a multifunctional drug in the cancer therapeutics [19] Figure 13.
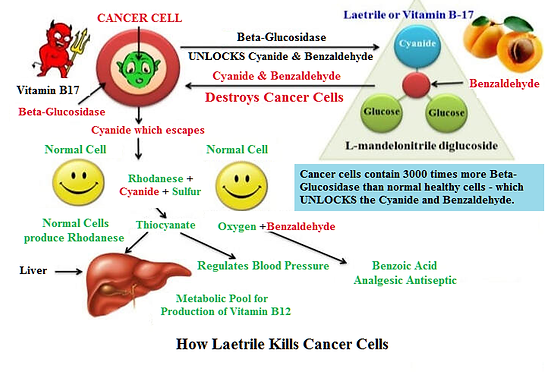
Figure 13: How Laetrile kills cancer cells
- In the August 2020 Current Molecular Pharmacology, researchers say they demonstrated that amygdalin could kill certain breast cancer cell lines and that amygdalin may prevent those cells from spreading throughout the body. They also state that it wasn’t toxic to healthy skin cells. [20]
- In a study published in the June 2020 International Journal of Nanomedicine, researchers combined amygdalin with an enzyme called beta-glucosidase (ß-glu), which enhances amygdalin activity, and found that it led to the death of prostate cancer cells. They say the treatment had some impact on heart and liver function but didn’t appear to cause organ damage. [21]
No Controlled Trials of Laetrile are available
No controlled clinical trials of laetrile have been reported. Anecdotal reports and case reports have not shown laetrile to be an effective treatment for cancer.
Benzaldehyde, which is made when laetrile is broken down by the body, has been tested for anticancer activity in people. In two clinical series, patients with advanced cancer who had not responded to standard therapy were treated with benzaldehyde. Some patients had a complete response, while some had a decrease in tumor size. The response to benzaldehyde only lasted during treatment. Most of the patients had been treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
The National Cancer Institute requested case reports from practitioners who believed their patients were helped by treatment with laetrile. An expert panel concluded that 2 of 67 patients had complete responses and 4 had a decrease in tumor size. Figure14.

Figure 14: National Cancer Institute
Findings from 2 clinical trials conducted by the National Cancer Institute reported the following:
- A phase I study tested doses, schedules, and ways to give amygdalin in 6 cancer patients. Researchers found that amygdalin caused very few side effects at the prescribed doses when given by mouth or by IV. Two patients who ate raw almonds while taking amygdalin had side effects.
- A phase II study with 175 patients looked at what types of cancer might benefit from treatment with amygdalin. Most of the patients in this study had breast, colon, or lung cancer. In about half of the patients, cancer had grown by the end of the treatment. Cancer had grown in all patients 7 months after treatment ended. Patients reported improved symptoms, such as the ability to work or do other activities. These improvements did not last after treatment ended. [22]
Kanematsu Sugiura’s work was banned by BIG Pharma Monopoly
Kanematsu Sugiura (1890 – October 21, 1979, in White Plains, New York) was a cancer researcher who spent his career at the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center. A pioneer in cancer research”, he completed over 250 papers before his death. Sugiura received a number of awards and prizes throughout his life and retired from the center in 1962.
He is perhaps best known for his work on laetrile, a controversial alternative cancer treatment, which he was convinced, had a palliative effect on certain mice tumors. The report that was released by Sugiura of his findings of the experiment are as follows: The results clearly show that Amygdalin (Laetrile) significantly inhibits the appearance of lung metastasis in mice bearing spontaneous mammary tumors and significantly increases the inhibition of the growth of the primary tumors. Laetrile also seemed to prevent slightly the appearance of new tumors. The improvement of health and appearance of the treated animals in comparison to controls is always a common observation. Dr. Sugiura has never observed complete regression of these tumors in all his cosmic experience with other chemotherapeutic agents. [25] Figure 15
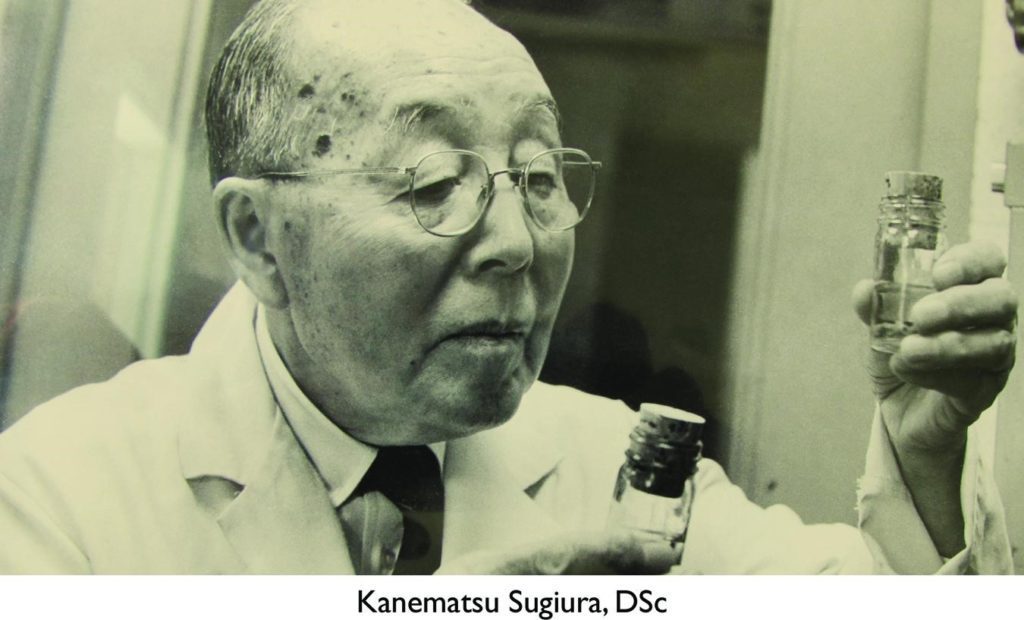

Figure 15: Kanematsu Sugiura
Dr Burzynski’s work on Antineoplastons got rejected by Rockefeller
Stanislaw Burzynski was a Doctor of Biochemistry who immigrated to the US from Poland in 1970, where he took up a position as a researcher and assistant professor at Baylor University in Houston, Texas. There, he discovered something which he called antineoplastons, naturally occurring “molecular switches” in the human body which, Burzynski asserted, the body used to control cancer growth. Burzynski and his clinic were investigated by local medical authorities for using “unapproved medications,” while the Rockefeller-founded American Cancer Society put antineoplastons on its “unproven methods” list, and those who had been funding his research pulled their support.
In 1983, the FDA filed a lawsuit to get him to shut down his operation, and when this failed, FDA agents and federal marshals simply raided the Burzynski Research Institute and seized over 200,000 confidential documents. Still Burzynski continued on. He raised millions of dollars through his Institute to pay for clinical trials for antineoplastons, money Big Pharma companies are more than happy to spend since they know they will recoup it when their products are patented. By the mid-90s, he was able to provide the FDA with sixty clinical trials, meeting the requirement for their Phase I testing. For another decade he worked, compiling hundreds more clinical trials, meeting the requirements for Phase II of testing on his own at the cost of millions of dollars. Figure 16.

Figure 16: Burzynski Research Institute
In 2011, Burzynski began Phase III testing, which involves thousands of participants and can last for years, again, at the cost of many millions of dollars. He was closing in on the finish line by 2013, which is when the FDA stepped in and put a stop to the trials. They complained that the Burzynski Research Institute was doing all of the testing, when, of course, this is simply how the FDA approval process works. The only difference is usually the testing is being done by a Big Pharma company. Figure 17.
Figure 17: Antineoplastons
Finally, in 2017, the FDA cancelled antineoplaston clinical trials for good, refusing Burzynski the right to even conduct the tests. Moreover, Burzynski had his medical license revoked and was fined hundreds of thousands of dollars for his trouble. The point made by Burzynski and his antineoplastons, by Sloan-Kettering’s Laetrile trials, is simple. It’s a case of ‘you’re damned if you do and damned if you don’t.’ If testing is conducted in a Rockefeller Big Pharma laboratory, it will be repeated and repeated and repeated until it gives the desired results, no matter how manipulated these results might be. And if you conduct the tests yourself, spending millions upon millions of dollars, the results will still not be accepted. Figure 18.

Figure 18: Dr Burzynski
Big Pharma controls the testing, they control approval, they control academic thought. But look closer, and it goes even further than that.
Big Pharma employs 1,270 registered lobbyists in the halls of government, more than two Big Pharma lobbyists for every member of congress, at a cost of over $200 million per year. They also spend tens of millions of dollars every year financing political campaigns, nearly every member of congress is funded by Big Pharma. On top of that, Big Pharma lobbyists and executives are repeatedly put in charge of the government bodies tasked with overseeing the pharmaceutical industry, like the FDA. Simply, the production and sale of medicine is tightly regulated by government, and Big Pharma controls the government. [23]
Big Pharma secrets
1. To develop drugs is not so expensive
Big Pharma inflates the costs of research and development (R&D) for new drugs to support their high prices, and frequently classifies “opportunity costs” and non-research activities, like the price of purchasing another firm, as R&D costs. While Big Pharma frequently asserts that developing a new drug costs US$2–3 billion, other reliable estimates are at least 10 times lower, in the $100–200 million range.
2. The pharmaceutical sector lacks innovation.
The market receives about two-thirds of new medications that are not any better than what is already available. Pharma companies spend more time creating ‘me-too’ medications than they do discovering novel treatments.
3. Patents are extended – over and over – to prolong monopolies
A well-known pharmaceutical strategy is called “patent evergreening,” in which companies apply for new patents on minor modifications to already-approved medications in order to extend their monopoly and prevent the availability of low-cost generic alternatives.
4. You are paying for your medications twice.
The majority of new pharmaceuticals and health technologies are developed in government and university laboratories, which are supported by public, tax-payer money. Tax rebates and other financial incentives are provided to them so they can “de-risk” their research efforts and privatize and patent the outcomes. Then they slap governments and taxpayers with hefty fees.
5. Pharma intimidates developing nations for defying its corporate interests.
Big Pharma frequently targets low- and middle-income nations like India, South Africa, Thailand, Brazil, Colombia, and Malaysia with coercive legal lawsuits for putting the interests of the public over that of the pharmaceutical industry. Pharma works aggressively to sway international trade laws in its favour, together with a few wealthy nations, even at the expense of public health. Pharma pockets more than they re-invest
6. Big Pharma says they need huge profits so they can pay for R&D and innovation. But in reality, they spend more on share buybacks to boost their own stock prices, and on sales and marketing, than on R&D. [11]
References
- https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/americanexperience/features/rockefellers-john/
- https://guides.loc.gov/this-month-in-business-history/january/standard-oil-established
- https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/americanexperience/features/rockefellers-john/
- https://meridianhealthclinic.com/how-rockefeller-created-the-business-of-western-medicine/
- https://www.abc.net.au/news/2012-02-21/schwager-war-against-natural-medicine/3840682
- Blaskiewicz, Robert (2013). “The Big Pharma conspiracy theory”. Medical Writing. 22 (4): 259. doi:10.1179/2047480613Z.000000000142.
- Ladini R (12 May 2021). “Religious and conspiracist? An analysis of the relationship between the dimensions of individual religiosity and belief in a big pharma conspiracy theory”. Italian Political Science Review/Rivista Italiana di Scienza Politica. 52 (1): 33–50. doi:10.1017/ipo.2021.15. eISSN 2057-4908. hdl:2434/843881. ISSN 0048-8402. S2CID 236584982.
- Radford, Benjamin. “Big Pharma Conspiracy Debunked”. centerforinquiry.org. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- Goldacre, Ben (2008). “Foreword”. Bad Pharma. Fourth Estate. ISBN 978-0-00-735074-2.
- Novella, Steven (22 April 2010). “Demonizing ‘Big Pharma'”. Science-Based Medicine.
- https://www.msf.org/6-things-big-pharma-doesn%E2%80%99t-want-you-know-access-medicines
- https://www.cochrane.org/CD005476/GYNAECA_laetrile-treatment-cancer
- Culbert M: Freedom From Cancer: The Amazing Story of Vitamin B7. or Laetrile. Seal Beach, Calif. 1976 Press, 1976. pp 78. 94—96
- Laetrile: The Commissioner’s Decision. The Federal Register. US Department of Health, Medical. Education and Welfare, Public Health Service, August 5. 1977, pp 8.
- https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.3322/canjclin.31.2.91
- NIH National Cancer Institute [Online]. 2016 July 14 [cited 2016 July 27]; Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/hp/laetrile-pdq
- Greenberg DM. The case against laetrile: the fraudulent cancer remedy. Cancer 1980;45:799-807. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/laetrile-amygdalin-89572
- Al-Khafaji K, Taskin Tok T. Understanding the mechanism of amygdalin’s multifunctional anti-cancer action using computational approach. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021;39(5):1600-1610. doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1736159
- Mosayyebi B, Mohammadi L, Kalantary-Charvadeh A, Rahmati M. Amygdalin decreases adhesion and migration of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines [published online ahead of print, 2020 Aug 10]. Curr Mol Pharmacol. doi:10.2174/1874467213666200810141251
- Zhou J, Hou J, Rao J, Zhou C, Liu Y, Gao W. Magnetically directed enzyme/prodrug prostate cancer therapy based on β-Glucosidase/amygdalin. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:4639-4657. Published 2020 Jun 29. doi:10.2147/IJN.S242359
- https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/patient/laetrile-pdq#:~:text=people%20with%20cancer.-,Laetrile%20is%20another%20name%20for%20amygdalin.,thought%20to%20kill%20cancer%20cells.
- https://universe-inside-you.com/rockefeller-big-pharma/
- https://www.archives.gov/milestone-documents/sherman-anti-trust-act#:~:text=The%20Sherman%20Anti%2DTrust%20Act%20authorized%20the%20federal%20government%20to,foreign%20nations%22%20was%20declared%20illegal.
- Hutchison DJ (July 1980). “Kanematsu Sugiura 1890-1979”. Cancer Res. 40 (7): 2625–6. PMID 6992988.
- https://www.britannica.com/topic/Standard-Oil
- https://guides.loc.gov/chronicling-america-standard-oil-monopoly
- https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/standard_oil_co._of_new_jersey_v._united_states_(1911)#:~:text=Primary%20tabs-,Standard%20Oil%20Co.,the%20company%20be%20geographically%20split.
- https://www.crf-usa.org/bill-of-rights-in-action/bria-16-2-b-rockefeller-and-the-standard-oil-monopoly.html
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/laetrile-vitamin-b17#TOC_TITLE_HDR_4
- https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/patient/laetrile-pdq
