
What is Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)?

Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a polypeptide tropic hormone. It’s also known as adrenocorticotropin and corticotropin. This peptide plays an important role in the body’s response to stress. We naturally make ACTH within the body, but sometimes the body doesn’t make enough and we must supplement with either natural or synthetic ACTH. This peptide plays a critical role in cortisol levels, which we will discuss in this article.
What is Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)?
The precursor molecule to ACTH is pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), which is a 241-amino acid molecule. From that, we get ACTH or corticotropin, which is a 39 amino acid peptide. Peptides are just strings of amino acids, similar to proteins, which are the building blocks of the body.
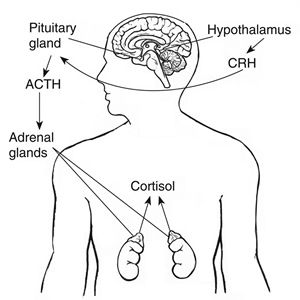
ACTH is a trophic hormone, meaning it can indirectly target cells by stimulating the endocrine system. When it occurs naturally in the body, ACTH is released in the brain by the pituitary gland, which is linked to the hypothalamus via a blood vessel system. The hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) which tells the anterior pituitary gland to release ACTH.
ACTH then targets the adrenal glands, which we find on top of each kidney. In response, the adrenal glands release cortisol and androgens. Cortisol is a key hormone for stress response, although it plays other roles, too. Meanwhile, androgens are a group of sex hormones.
Altogether, the body naturally uses ACTH to regulate cortisol and androgen production. When we feel mental or physical stress, the body produces ACTH to increase cortisol levels. Unfortunately, sometimes these processes don’t work properly, causing imbalances that lead to disease.
What Role Does ACTH Play in the Body?
To understand the importance of ACTH, we must first discuss cortisol. Although it’s known as the stress hormone, it has many functions. It also helps with:
- Controlling the use of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in the body
- Regulating the metabolism
- Managing proper blood pressure
- Regulating blood sugar
- Controlling the sleep-wake cycle
- Suppressing inflammation
On the other hand, ACTH also stimulates the release of androgens – sex hormones. Additionally, it begins the process of increasing hormones like adrenaline and noradrenaline by producing certain chemical substances.
When ACTH levels are abnormal, we see issues related to high or low cortisol. Low levels of ACTH can lead to:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Muscle weakness
- Low blood pressure
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
High levels of cortisol can result in:
- Weight gain
- Fat buildup in the shoulders
- Increases in body hair
- Fatigue
- Acne
- Stretch marks on the midsection, thighs, and breasts
- Easily bruising skin
Low or high levels of ACTH can lead to more serious conditions and diseases, including:
- Ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone tumor
- Primary adrenal insufficiency
- Cushing’s disease
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Hypopituitarism
The Uses of ACTH as a Medication

If your doctor suspects that you have low ACTH levels, they’ll order a simple blood test. That will measure the levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone levels in your blood. Your doctor may also order a cortisol test to check for related issues in your adrenal and pituitary glands. An ACTH stimulation test may also be needed to test how well the adrenal glands respond to ACTH.
ACTH may be given as a medication in a couple of forms. Corticotropin is purified from the pituitary glands of pigs. This is the natural way to get this polypeptide tropic hormone. Alternatively, we can also make a synthetic version, which goes by several names: tetracosactide, synacthen, cosyntropin, and tetracosactrin. The synthetic version is a shorter peptide, consisting of the first 24 of the 39 total amino acids in ACTH. Despite its shorter length, it still maintains the full function of ACTH.
These medications are given via injection and can treat a variety of ACTH-related issues. It’s worth noting that they have different approvals in different countries. For example, in the US, tetracosactide is permitted only for diagnosis via the ACTH test, whereas the UK allows it to be used for therapeutic purposes.
Meanwhile, corticotropin is used to treat many conditions in the US, including:
- Epileptic spasms in infants
- Acute episodes of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and multiple sclerosis
- Collagen disorders, like lupus and systemic dermatomyositis
- Skin conditions, like Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Serum sickness
- Eye conditions
- Lung conditions
- Kidney conditions
Taking corticotropin or tetracosactide comes with few adverse effects. However, it may make you more likely to get infections. It also increases your risk of developing Cushing’s syndrome and hypothalamic-pituitary-axis (HPA) suppression.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone is critical to human health. Be sure to work with your primary care physician before using this medication or schedule a consultation with one of our health consultants.
KIYA Longevity provides innovative best-in-class peptide products that meet the highest standards for safety and purity at a fraction of the cost.
FAQs: Understanding ACTH and its Impact
Why is ACTH important?
ACTH is the key messenger that tells your adrenal glands to release cortisol, the “stress hormone.” It’s a crucial part of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis), which regulates everything from stress response to metabolism.
What triggers ACTH production?
The hypothalamus in your brain produces a hormone called CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone). CRH stimulates adrenocorticotropic hormone production in your pituitary gland.
How is ACTH tested?
An ACTH test involves a blood sample to measure both ACTH and cortisol levels. This can help doctors understand if the issue lies with the adrenal glands, the pituitary gland, or somewhere else within the feedback loop.
What do abnormal ACTH levels mean?
High ACTH with high cortisol could indicate issues like Cushing’s disease (sometimes caused by a pituitary tumor) or an adrenal tumor. High ACTH with low cortisol usually points to a primary adrenal gland problem (like Addison’s disease). Low ACTH with low cortisol could indicate a problem within the hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
Can other hormones affect ACTH levels?
Yes! Besides cortisol itself providing feedback, other hormones, medications, and health conditions can influence both ACTH production and its actions within the body.
What does it mean if I have too much cortisol?
Chronically high cortisol levels can lead to various health problems including weight gain, high blood pressure, weakened immune function, and even mood disorders. Your doctor can help diagnose if high cortisol is a concern and work with you on managing it.
Can a pituitary tumor affect ACTH production?
Yes, some pituitary tumors can overproduce ACTH, leading to excessively high cortisol levels (Cushing’s disease). ACTH testing, along with imaging, can help identify if this is the cause of abnormal cortisol levels.
PEPTIDE)BPC-157 PURE PEPTIDE (IMMEDIATE
RELEASE)BPC-157 PURE Oral Spray (RAPID
ABSORPTION)KPV PEPTIDE (RAPID ABSORPTION)TB4-FRAG MAX PEPTIDE (HEALING AND
RECOVERY)THYMOGEN ALPHA-1 (IMMUNE SUPPTORT)Weight Loss Peptide “Can’t Weight”
Questions about other peptides? Check out Kiya Longevity’s Peptide Guide.
Resources:
https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/adrenocorticotropic-hormone-acth/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500031/
https://www.acthar.com/Static/pdf/Acthar-PI.pdf
